Publicado en: CARTILAGE
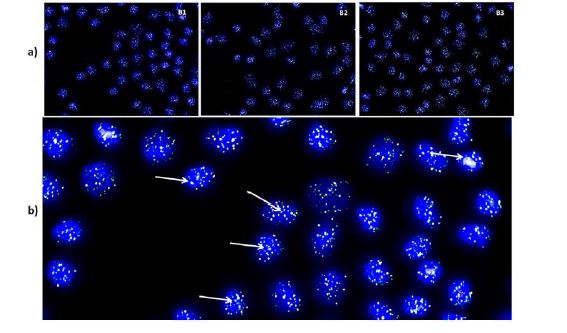
Abstract. In the process of cell division, the extremes of the eukaryotic chromosomes are progressively shortening, and this phenomenon is related to cell degeneration and senescence. The treatment of cartilage lesions with autologous chondrocytes implies that cells proliferate in an artificial environment. We have studied the viability of cultured chondrocytes after measurement of their telomere length before implantation. Methods. Articular cartilage biopsies (B1, B2, and B3) were obtained from 3 patients (2 males and 1 female) with knee cartilage defects, who were going to be treated with chondrocyte implantation. Chondrocytes were cultured in DMEM with autologous serum. After the third passage, an aliquot of 1 million cells was removed to estimate the telomere length and the remaining cells were implanted. Telomere length was measured by quantitative fluorescent in situ hybridization (Q-FISH). Patients’ clinical outcome was determined preoperatively, and 12 and 24 months postimplantation with the International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC) questionnaire. Results. After chondrocyte implantation, IKDC score doubled at 12 and 24 months with regard to the basal value. After 3 passages, chondrocytes were cultured for a mean of 45.67 days, the mean duplication time being 4.53 days and the mean number of cell divisions being 10.04 during the culture period. The 20th percentile of telomere lengths were 6.84, 6.96, and 7.06 kbp and the median telomere lengths 10.30, 10.47, and 10.73 kbp, respectively. No significant correlation was found between IKDC score and telomere length. Conclusion. Culturing autologous chondrocytes for implantation is not related to cell senescence in terms of telomere length.
Referencia:
Juan Manuel López-Alcorocho, Isabel Guillén-Vicente, Elena Rodríguez-Iñigo, Marta Guillén-Vicente, Tomás Fernando Fernández-Jaén, Rosa Caballero, Mercedes Casqueiro, Pilar Najarro, Steve Abelow, and Pedro Guillén-García